Allergies – Treatment Methods. ASIT therapy
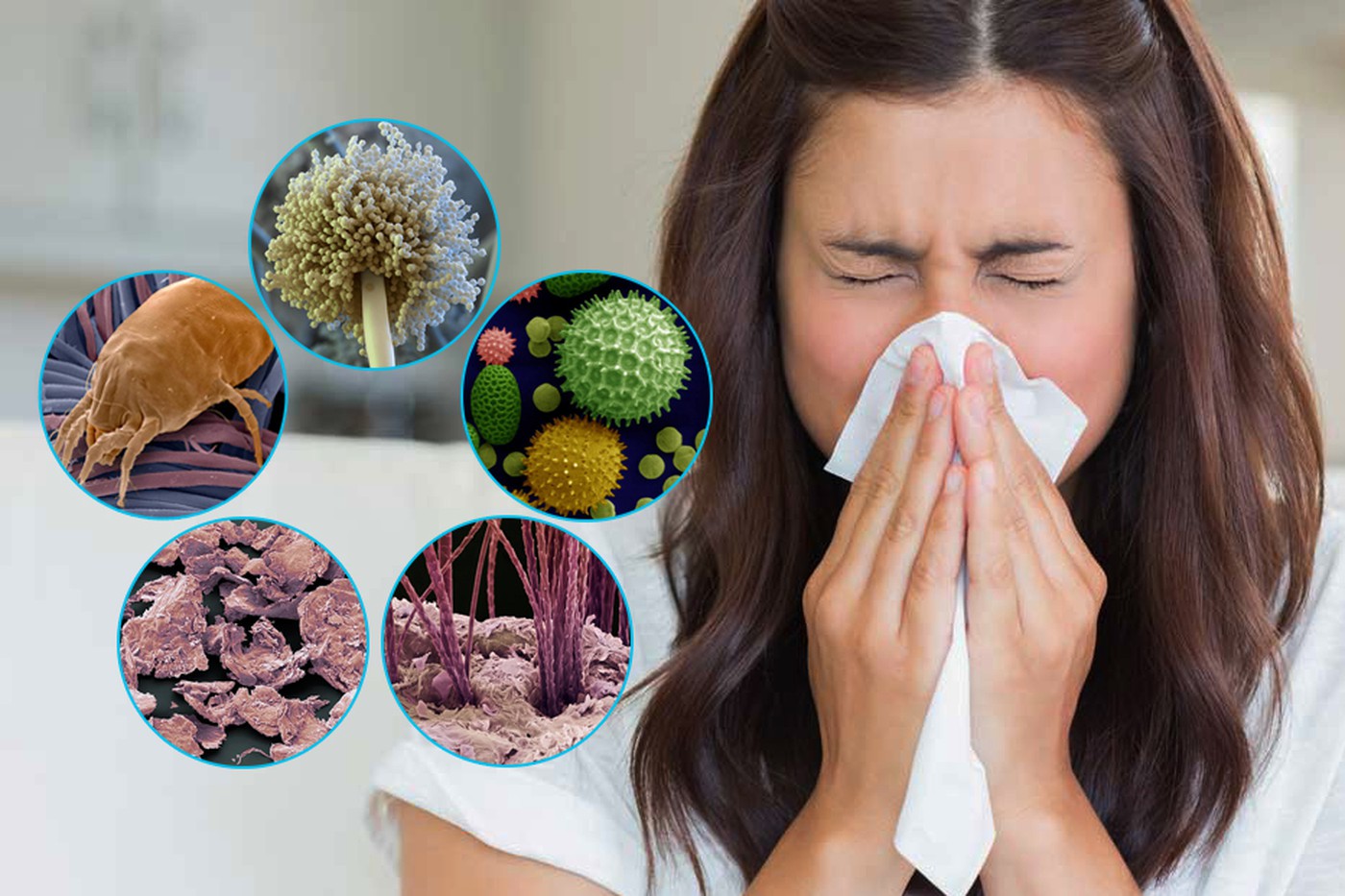

Allergy is an unusual sensitivity to various substances that do not cause painful reactions in most people. The answer to why some people have allergies, while others do not, lies in the peculiarities of the immune system of each person.
Immunity is a term that characterizes the body’s ability to recognize and destroy everything that is perceived by the human immune system as “alien”, and therefore harmful to health. Such enemies can be viruses that cause flu, SARS and other infections, as well as bacteria – the cause of tonsillitis, pneumonia, etc., poisons, fungi. For the immune system of some people, house dust, pollen, mold, certain types of food, etc., become enemies. Then these substances become allergens, and the person develops an allergy. In response to such interference, our body produces protective antibody proteins that attack and neutralize these hostile elements.
Allergic diseases, what are they?
Food allergy is a condition of increased sensitivity of the body to food products. Symptoms: acute urticaria, atopic dermatitis, various disorders of the digestive system.
Pollinosis is an allergy to pollen. It manifests itself as sneezing, watery nasal discharge, lacrimation, itching, sometimes swelling of the eyes, unpleasant painful sensations in the mouth and throat, in severe cases – attacks of suffocation.
Bronchial asthma is the most severe manifestation of an allergic respiratory disease. Bronchial asthma may not be allergic, but in this case we will only touch on allergic asthma. In asthma, as a rule, there is an allergic inflammation of the respiratory system, from the nasal mucosa to the smallest bronchi and bronchioles. The main symptom of bronchial asthma – difficulty breathing – is a direct consequence of the compression of the smooth muscles of the bronchi, which entails other structural changes.
How is allergy diagnosed?
Obviously, there are certain symptoms, such as sneezing, runny nose, watery eyes, rashes, redness of the skin, which we associate with allergies. However, there are many other diseases that have similar manifestations. In order to determine what kind of disease caused these symptoms, it is imperative to see a doctor. In addition to examination and questions, the doctor has several more accurate and objective methods to confirm the diagnosis (skin tests with allergens, blood test – laboratory test with allergens). When the question arises of choosing a method for determining the “culpable” allergens: skin testing or blood tests, the final decision is always made by the doctor, whose main task is to ensure the safety of the patient.
How are allergies treated?
Each person is individual, he is characterized by a certain intensity of symptoms and the severity of the disease, which is extremely important for the choice of treatment tactics.
Today in the world there are three main ways to deal with allergic diseases:
Stopping or reducing contact with the allergen or irritant.
Using medications to relieve symptoms.
Allergen specific immunotherapy (ASIT)
Unfortunately, none of the drugs used to relieve allergy symptoms can change the body’s response to the allergen. Allergic diseases often develop incrementally: first, these are mild manifestations of rhinitis, then they become more pronounced, then dry cough and asthma attacks may join – bronchial asthma develops in 50% of cases of allergic rhinitis. Another feature of allergies is that medications, which initially relieve all symptoms well, eventually cease to help. In addition, the reaction season may lengthen – for example, if at first the body reacts to pollen, when its concentration in the air reaches its highest point, then later the symptoms will bother you during the entire flowering period. And the most unpleasant thing is that against the background of pronounced sensitivity to one allergen, a reaction to new irritants can join – for example, grass pollen or house dust mites.
ASIT is the only method to date that can change the body’s attitude to the allergen and prevent the further development of allergies. This method has been used all over the world for a long time, and is the most modern and effective.
Allergen-specific immunotherapy reduces the body’s sensitivity to the allergen to which it has a reaction. The patient receives a series of injections with microdoses of allergens hostile to him (house dust, house dust mite, pollen) in a gradual increasing concentration, as a result of which the resistance to these allergens increases.
This is the only method that not only relieves symptoms, but also eliminates the cause of allergies – an inadequate response of the immune system to the external environment. ASIT treatment is most commonly used in patients with pollen allergies. Unlike food or household allergies, where you can limit contact with the allergen, with hay fever it is impossible to completely get rid of contact with pollen allergens during the flowering season. Carrying out ASIT therapy before the flowering season allows you to spend this period without drugs and unpleasant symptoms.
The choice of the allergen (s) for ASIT is carried out on the basis of the specific allergological diagnostics previously carried out to the patient. After the exact determination of the allergen, the drug for treatment is selected, the method of administration and the duration of therapy are determined.
The optimal age of patients for whom ASIT is recommended ranges from 5 to 50 years. The earlier treatment is started (at an early stage of the disease), the higher the likelihood of a good effect.
ASIT can significantly weaken the clinical manifestations of hay fever and reduce the likelihood of its transition to more severe forms, in particular, to bronchial asthma.
Contraindications for ASIT:
Exacerbation of an allergic disease
Active tuberculosis
Active rheumatism
Ischemic heart disease in the acute phase
Circulatory failure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circulatory_collapse
Hepatitis, nephritis in the acute phase with signs of dysfunction of these organs
Diseases of the blood
Diseases of the thyroid gland
The presence of foci of active infection
Mental illness
Oncological diseases
Fibroids of the uterus, polyps, etc.